Organelles, microscopic structures inside cells, are essential for the functioning and survival of living organisms. While many organelles are present in both plant and animal cells, there are a few remarkable ones that are exclusively found in plants. These intriguing plant-specific organelles play vital roles in various physiological processes, enabling plants to thrive and adapt to their environment. Their uniqueness offers insight into the special adaptations plants possess, making them so distinct and fascinating compared to other organisms. Let’s embark on a journey to explore these exceptional organelles that are exclusive to the botanical world.
key Takeaways
- Chloroplasts are organelles found only in plant cells that are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy.
- Vacuoles, which are large membrane-bound sacs, are unique to plant cells and perform various functions such as storing water, nutrients, and waste products.
- The cell wall is a rigid structure found only in plant cells, providing support and protection, and giving plants their characteristic shape.
- Plastids are a group of organelles found in plant cells, including chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and amyloplasts, each playing a specific role in plant metabolism.
- Peroxisomes are organelles found in plant cells that play a vital role in detoxifying harmful substances and breaking down fatty acids.
- Glyoxysomes, specialized organelles only found in the cells of germinating plants or oily seeds, aid in the conversion of stored lipids into usable energy.
- Proteinoplasts, or leucoplasts, are non-pigmented plastids found in plant cells that store proteins or synthesize fatty acids and amino acids.
Organelles Unique to Plants
In the world of biology, a variety of organelles can be found within the cells of different organisms. While certain organelles are common to both animals and plants, there are some organelles that are exclusively found in plants. These unique plant organelles play crucial roles in the various biological processes and functions specific to plant cells.
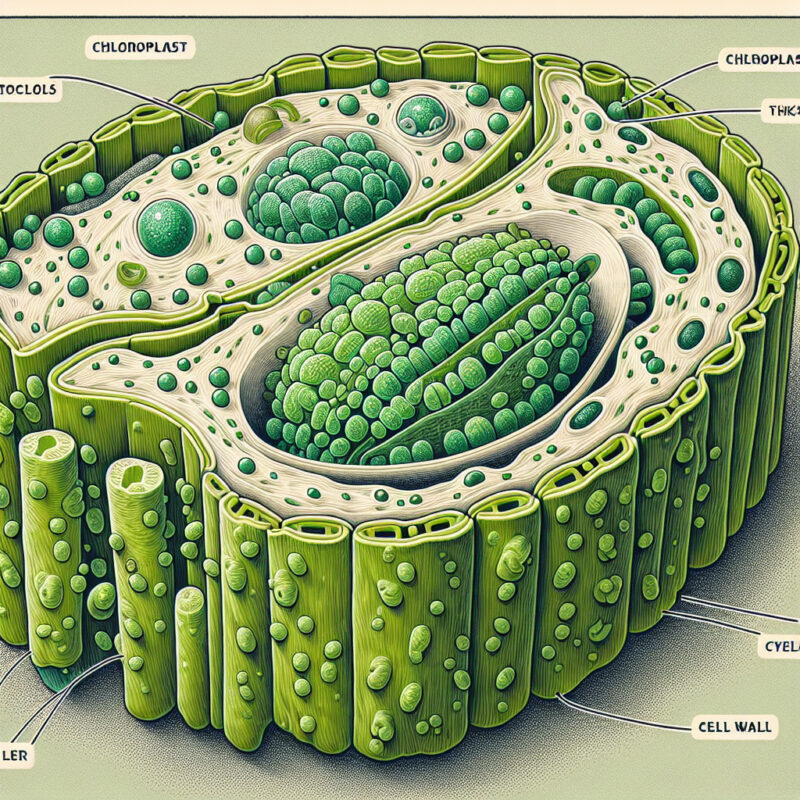
Chloroplasts
One of the most well-known organelles unique to plants is the chloroplast. Chloroplasts are responsible for the process of photosynthesis, which converts light energy into chemical energy. This conversion allows plants to use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose and oxygen. Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll, a pigment that gives plants their green color and is essential for capturing light energy.
Central Vacuole
The central vacuole is another organelle that is only found in plant cells. It is a large, fluid-filled sac that occupies a significant portion of the plant cell’s volume. The central vacuole acts as a storage area for various substances, including water, ions, sugars, pigments, and toxins. It also helps maintain turgor pressure, which is crucial for plant rigidity and support. Moreover, the central vacuole is involved in storing waste products and regulating the concentration of ions within the cell.
Cell Wall
Unlike animal cells, plant cells possess a cell wall, which is an additional layer outside the plasma membrane. The cell wall provides structural support and protection to the cell. It consists mainly of cellulose, a complex sugar polymer that forms a rigid and tough meshwork. The cell wall helps maintain cell shape, prevents excessive water uptake, and plays a critical role in plant growth and development.
Plasmodesmata
Plasmodesmata are unique channels that connect adjacent plant cells. These narrow channels traverse the cell wall, allowing the exchange of various substances such as water, ions, sugars, and hormones between cells. Plasmodesmata play a vital role in intercellular communication, facilitating the coordination of activities in different parts of the plant.
Conclusion
Plant cells possess several organelles that are not found in animal cells. The chloroplasts enable plants to conduct photosynthesis and convert light energy into chemical energy. The central vacuole serves as a storage compartment and regulates various cell processes. The cell wall provides structural support and protection, while plasmodesmata allow communication between adjacent plant cells. These unique organelles collectively contribute to the distinctive characteristics and physiology of plant cells.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the organelles that are only found in plants?
The organelles that are exclusively found in plant cells are chloroplasts, cell walls, and central vacuoles. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Cell walls provide structural support and protection to plant cells. Central vacuoles store water, nutrients, and waste materials.
2. Why are these organelles only found in plants?
These organelles are only found in plants because they serve specific functions that are crucial for the survival and growth of plants. Chloroplasts, for example, contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures sunlight and plays a vital role in photosynthesis. Cell walls provide rigidity and support to plant cells, allowing them to maintain their shape and withstand external pressures. Central vacuoles, on the other hand, help maintain turgor pressure, regulate cell growth, and store essential molecules.
3. Can these organelles be found in other organisms?
No, these organelles are unique to plant cells and cannot be found in other organisms. While other organisms have their own set of organelles with different functions, chloroplasts, cell walls, and central vacuoles are specifically adapted to meet the needs of plant cells and are not present in animal or bacterial cells.
4. How do these organelles contribute to the overall function and structure of plants?
Chloroplasts play a crucial role in providing plants with the ability to produce their own food through photosynthesis. This process enables plants to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. The cell wall provides strength and support to plant cells, helping them maintain their shape, protect against mechanical stress, and resist diseases and pests. Central vacuoles aid in maintaining the osmotic balance of the plant cell, regulating the concentration of solutes and water and assisting in the growth and development of the plant.
5. Are there any other unique features of plant cells?
Aside from the organelles mentioned, plant cells have other unique features such as plasmodesmata, which are cytoplasmic channels that connect adjacent plant cells, allowing for the exchange of nutrients, water, and chemical signals. Additionally, plant cells may possess specialized organelles called peroxisomes, which are involved in various metabolic processes, including the breakdown of fatty acids and the detoxification of harmful substances.