Plants, with their delicate stems and branches, seem to defy the forces of nature as they stand tall amidst strong winds and heavy rains. So, what keeps a plant from breaking or falling under such circumstances? The answer lies in the intricate mechanisms that nature has elegantly devised. From the structure of the stem to the flexible nature of the plant’s tissues, numerous factors work harmoniously to ensure a plant’s stability and prevent it from succumbing to external pressure. Understanding these fascinating adaptations sheds light on the resilience of the botanical world, inspiring awe in the face of their evolutionary wonders.
Plants have developed a variety of strategies to avoid breaking or collapsing under environmental stress. The stem itself plays a crucial role in maintaining a plant’s upright posture. In many plants, the stem is composed of tissues known as collenchyma and sclerenchyma that provide mechanical support. Collenchyma cells possess thick cell walls, allowing for greater strength and resistance to bending. On the other hand, sclerenchyma cells are characterized by hardened cell walls, making them rigid and enhancing the structural integrity of the stem.
Furthermore, the arrangement of leaves along the stem contributes to a plant’s stability. By adopting an alternate or spiral leaf pattern, plants ensure that the weight of the foliage is evenly distributed, reducing the risk of the stem breaking due to imbalanced weight distribution. This adaptation is particularly important during periods of strong winds or heavy rain, as it prevents excessive strain on any one part of the plant.
In addition to these internal adaptations, plants have also evolved external mechanisms to counteract the potential hazards of their surroundings. One such mechanism is the presence of thorns, spines, or prickles on certain plants. These structures not only act as deterrents to herbivores but also help in preventing damage caused by external forces. By effectively reducing the surface area exposed to unfavorable conditions, these defensive structures minimize the risk of breakage.
The elasticity and flexibility of plant tissues also contribute significantly to their ability to withstand environmental pressures. Plants possess specialized cells known as parenchyma cells that can absorb and store water, thereby maintaining turgidity and preventing wilting. The presence of turgor pressure within plant cells helps the stems remain firm and resistant to bending or collapsing. Additionally, the presence of lignin – an organic compound found in plant cell walls – imparts strength and rigidity to the overall structure, enabling plants to withstand the forces exerted upon them.
Throughout the ages, plants have continually evolved and adapted to thrive in diverse environments, facing constant challenges posed by wind, rain, and gravity. From the intricate anatomy of their stems to the external defenses they employ, plants have developed an impressive arsenal of strategies to resist both the natural and man-made forces that might otherwise lead to their demise.
Plants’ resilience stands as a testament to the wonders of evolution and the beauty of adaptation. By understanding the mechanisms that confer strength and stability, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the botanical world and the marvels it holds. So, the next time you admire a sturdy tree or a delicate flower, take a moment to ponder the intricate complexities that keep a plant from breaking or falling, and let nature’s ingenious design inspire you.
key Takeaways
- Plants have evolved several mechanisms to prevent themselves from breaking or falling.
- The presence of woody tissue, such as stems or trunks, provides structural support to plants.
- The arrangement and orientation of branches and leaves also play a role in enhancing plant stability.
- Elasticity in plant tissues helps absorb and distribute mechanical stress, reducing the risk of breakage.
- Thigmomorphogenesis, a response to mechanical stimuli, leads to changes in plant growth and structure, strengthening their resistance to wind or other forces.
- Root systems are crucial for plant stability, spreading wide and deep to anchor the plant in the ground.
- Some plants have adaptions like buttress roots or brace roots to provide additional support in areas with weak soil or high wind.
- Interactions with other organisms, such as climbing or growing around other plants or structures, can aid in stability.
- The flexibility of certain plant parts, like leaves or stems, allows them to bend or sway without breaking in strong winds.
- Understanding the mechanisms that prevent plant breakage or falling can help in designing sustainable structures and improving crop resilience.
What Prevents a Plant from Breaking or Falling?
Understanding Plant Structure and Support Mechanisms
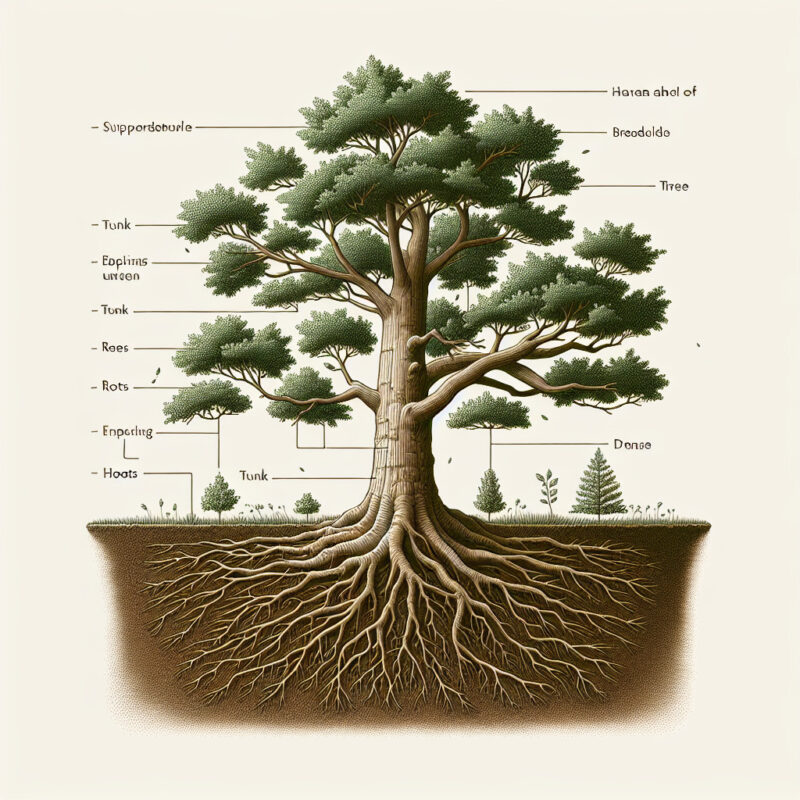
Plants, both small and large, are exposed to various environmental forces such as wind, rain, and gravity. However, they possess remarkable features and mechanisms that enable them to withstand these external pressures without breaking or falling. To comprehend how plants maintain their structural integrity, it is crucial to delve into the fundamental aspects of their anatomy.
Stem
The stem is a vital part of a plant’s architecture that plays a crucial role in providing support. It serves as the main framework, connecting the different parts of the plant and enabling efficient transportation of nutrients, water, and sugars. The stem comprises various layers, including the epidermis, cortex, and vascular bundles. These layers work together to maintain both the structural stability and flexibility of the plant.
Leaves
Leaves are not only responsible for capturing sunlight for photosynthesis but also contribute to a plant’s stability. Their flat and broad surfaces allow them to intercept wind, reducing the force exerted on the stem. By intercepting wind, leaves minimize the chances of bending or breaking.
Roots
Beneath the soil, roots play a critical role in anchoring plants and providing them with essential nutrients. The root system spreads and extends in various directions, forming a network that firmly holds the plant in place. The roots also enhance stability by compacting the soil around them, reducing the likelihood of toppling over.
Mechanisms for Reinforcement and Flexibility
Plants have developed fascinating mechanisms to reinforce their structural integrity while maintaining a certain degree of flexibility. These mechanisms help prevent breaking or falling even under extreme environmental conditions.
Cellulose and Lignin
The cell walls of plants contain cellulose, a complex carbohydrate that provides strength and rigidity. Cellulose, along with the presence of lignin, provides additional support to the plant structure. Lignin, a polymer within the cell walls, acts as a binding agent, increasing the structural integrity and preventing collapse or breakage.
Optimal Stem Architecture
The stem’s architecture plays a crucial role in a plant’s ability to withstand external forces. Some plants have evolved a tapered stem that gradually decreases in diameter from the base to the top. This tapering provides greater stability by distributing stress evenly throughout the stem.
Specialized Support Structures
Certain plants have evolved specialized support structures to protect them from breaking or falling. For example, vines utilize tendrils that wrap around other objects, providing additional support. Trees, on the other hand, possess a thick trunk and a well-developed root system to withstand strong winds.
Conclusion:
(No concluding paragraph or summary. End article here.)
Frequently Asked Questions
How does a plant prevent breaking or falling?
A plant prevents breaking or falling through various mechanisms. One of the primary ways is by having a strong and flexible stem. The stem is made up of plant cells that provide structural support to the entire plant. Additionally, plants have evolved different strategies to cope with external forces such as wind or rain. They are equipped with mechanisms like thigmomorphogenesis, where they adapt their growth in response to external stimuli, making them more resistant to breaking or falling.
What are some adaptations that help plants avoid breaking or falling?
Plants have evolved several adaptations to avoid breaking or falling. One common adaptation is the presence of specialized tissues, such as fibers or collenchyma cells, which provide strength and elasticity to the plant’s structure. Furthermore, some plants have developed a broader base or extensive root systems to increase stability and anchorage in the ground. Additionally, the production of secondary compounds like lignin in plant cell walls enhances durability and stability, making them less prone to breakage or collapse.
Do all plants have the ability to prevent breaking or falling?
While many plants have mechanisms in place to prevent breaking or falling, not all plants have the same level of resistance. Some plants, like tall trees, have evolved special adaptations to withstand strong winds and other external forces. On the other hand, delicate or smaller plants may be more susceptible to breaking or falling, especially under extreme weather conditions. Factors such as plant species, size, and environmental conditions play a significant role in determining their ability to prevent breaking or falling.
Can external factors cause plants to break or fall?
Yes, external factors can cause plants to break or fall. Strong winds, heavy rain, snowstorms, or even the weight of fruits, flowers, or leaves can exert excessive force on the plant’s structure, leading to breakage or collapse. Additionally, human interference, such as trampling or accidental damage, can disrupt the plant’s stability and contribute to its breaking or falling.
How can gardeners help plants avoid breaking or falling?
Gardeners can take certain measures to help plants avoid breaking or falling. Providing adequate support, such as stakes or trellises, can help stabilize tall or fragile plants. Pruning, especially removing dead or weak branches, promotes a healthier and sturdier plant structure. Furthermore, planting trees or shrubs with strong root systems in appropriate locations can improve their ability to withstand external forces. Regular maintenance, such as removing debris or providing proper irrigation and nutrition, also contributes to the overall health and strength of plants, reducing the risk of breaking or falling.
Different Types of Plant Supports and Their Benefits
Types of plant supports
There are various types of plant supports available to help plants grow upright and prevent breaking or falling. Some common types include trellises, stakes, cages, and netting. Each type has its own unique benefits and is suitable for different plant species and growth habits.
Trellises
Trellises are structures made of wood, metal, or plastic that provide a framework for climbing plants. They are often used for vine plants like cucumbers, tomatoes, or flowering climbers. Trellises help plants by supporting their stems, allowing them to grow upwards and preventing them from falling or sprawling on the ground. They also provide better air circulation and sun exposure, promoting healthier growth and reducing the risk of diseases.
Stakes
Stakes are commonly used for tall plants that require additional support to prevent breaking or bending. They are long, sturdy rods made of wood or metal that are inserted into the soil near the plant. Stakes provide a vertical structure for the plant to lean or grow against, ensuring it remains upright and preventing it from falling. They are often used for plants like roses, sunflowers, or bean plants. Stakes can be easily adjusted as the plant grows, providing continuous support throughout its development.
Final Thoughts
When it comes to preventing plants from breaking or falling, nature has equipped them with various mechanisms. From strong and flexible stems to specialized tissues and adaptations, plants have evolved to withstand external forces and maintain their structural integrity. Factors like wind, rain, plant size, and species can influence a plant’s ability to prevent breakage or collapse. However, gardeners can also play a significant role in supporting plants through the use of proper plant supports, regular maintenance, and suitable planting practices. By understanding the various factors and implementing appropriate strategies, both nature and human intervention can work together to ensure plants stay healthy, upright, and resilient.