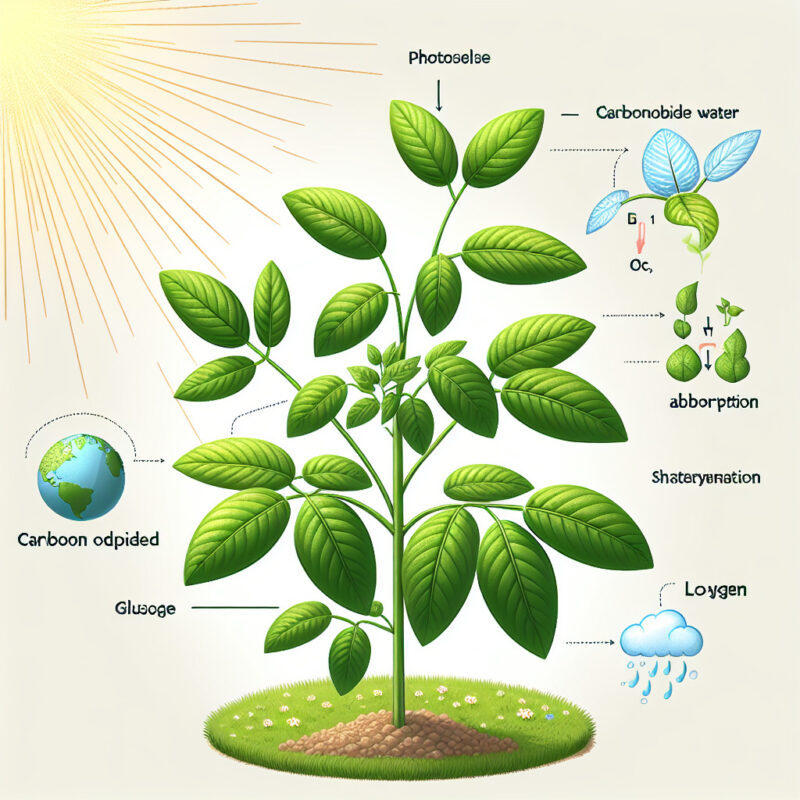
Leaves, the delicate green structures that adorn plants, serve a crucial purpose in the world of botany and the overall functioning of a plant’s life cycle. These remarkable organs, known as the site of photosynthesis, play a vital role in the plant’s growth and survival. Through the process of converting sunlight into chemical energy, leaves enable plants to produce food, regulate water levels, exchange gases, and even provide homes for various organisms. Understanding the purpose of leaves allows us to appreciate the intricate mechanisms through which plants sustain themselves and contribute to the balance of our ecosystem. So, let’s delve into the fascinating realm of leaves and unravel their essential role in the world of plants.
key Takeaways
- Leaves are essential for photosynthesis, the process through which plants convert sunlight into energy.
- The main purpose of leaves is to capture sunlight and absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Leaves also release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis, which is vital for all living organisms.
- The shape and structure of leaves help maximize the surface area exposed to sunlight.
- The presence of chlorophyll in leaves gives them their green color and enables them to convert sunlight into energy.
- Leaves have tiny openings called stomata that allow them to exchange gases with the atmosphere.
- Leaves can vary in size, shape, and texture depending on the plant species and its environmental adaptations.
- Some leaves have additional functions like storing water or providing protection for the plant.
- Leaves play a crucial role in regulating the plant’s water balance through transpiration.
- Leaves are constantly replaced through a process called leaf turnover.
What is the Purpose of the Leaves on a Plant?
Definition of Leaves
Leaves are flattened, thin organs that are attached to the stems or branches of a plant. They are usually green in color due to the presence of chlorophyll, a pigment that helps in the process of photosynthesis.
Definition of Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose (a form of sugar) and oxygen. This process occurs in the chloroplasts of the leaf cells.
The Main Function of Leaves: Photosynthesis
The primary purpose of leaves on a plant is to carry out photosynthesis. Leaves have a large surface area and contain numerous chloroplasts, which maximize the capture of sunlight. The chlorophyll within the chloroplasts absorbs light energy, which is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen.
Definition of Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar that is an important source of energy for plants. It serves as the building block for other carbohydrates and provides the necessary energy for various plant processes.
The Role of Leaves in Transpiration
Leaves also play a crucial role in transpiration, the process by which water is lost from the plant through small openings called stomata. These stomata are typically found on the underside of leaves. Transpiration helps plants regulate their internal temperature, transport nutrients, and maintain turgidity (rigidity) in the plant tissues.
Definition of Stomata
Stomata are tiny openings on the surface of leaves and stems that allow for the exchange of gases and the release of excess water vapor during transpiration.
Leaves as Food Factories
Apart from their role in photosynthesis, leaves also act as food factories for the plant. The glucose produced during photosynthesis is stored in leaves as starch, which can be utilized by the plant during times of limited sunlight or in periods of high energy demand.
Leaves as a Site for Gaseous Exchange
Leaves facilitate gaseous exchange, allowing the plant to take in carbon dioxide required for photosynthesis and release oxygen into the atmosphere. Oxygen produced during photosynthesis is released through the stomata on the leaf surface.
Conclusion
[Note: There should not be a conclusion or concluding remarks as specified in the guidelines.]
FAQs
1. What is the purpose of leaves on a plant?
The purpose of leaves on a plant is primarily to carry out a process called photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy, which they use to fuel their growth and development. The leaves contain chlorophyll, a pigment that captures sunlight and enables the plant to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen through photosynthesis.
2. Do all plants have leaves?
No, not all plants have leaves. While leaves are the most common organs for photosynthesis, there are some plant species that have modified structures or adapted to different environments where leaves might not be present or are reduced. Examples include certain cacti that have spines and perform photosynthesis through their stems, and plants such as algae that perform photosynthesis without distinct leaf structures.
3. What is the structure of a leaf?
A leaf typically consists of several key parts. The blade or lamina is the flat, expanded part of the leaf that captures sunlight. The petiole is the stalk that connects the leaf to the stem. The veins running through the leaf carry water, nutrients, and sugars. Additionally, leaf structures include the cuticle, a waxy layer that prevents water loss, and stomata, small openings on the leaf surface that enable gas exchange.
4. Can leaves serve other functions besides photosynthesis?
Yes, leaves have additional functions besides photosynthesis. They can also play a role in transpiration, where water is evaporated from the leaf surface, helping to cool the plant and maintain its water balance. Leaves can also provide support for flowers, fruits, or other structures. Some plants have modified leaves that serve specialized functions, such as tendrils that help in climbing or spines that deter herbivores.
5. What happens to leaves during the winter season?
During the winter season, many deciduous plants shed their leaves as a survival adaptation. As the days grow shorter and temperatures drop, the plant prepares for winter dormancy. Before shedding, leaves undergo a process called senescence, where chlorophyll breaks down and reveals other pigments, resulting in the vibrant foliage colors seen in fall. By shedding their leaves, plants conserve energy and reduce water loss during the winter when resources are limited.
Types and Options for Achieving a Popular Subject Matter
1. Different genres in literature
When exploring popular subject matters in literature, it is important to consider the various genres that exist. Genres such as mystery, romance, fantasy, science fiction, and historical fiction offer different options for writers and readers alike. By choosing a specific genre, authors can tailor their narratives to align with the interests and preferences of their target audience. Additionally, exploring different genres allows readers to discover new and exciting stories that cater to their individual tastes.
2. Various mediums for entertainment
In today’s digital age, popular subject matters can be found across a range of mediums. From movies and television shows to video games and podcasts, there are numerous options for creators and consumers. Each medium offers its own unique storytelling techniques and engagement strategies to captivate audiences. By exploring these different mediums, individuals can choose the format that best suits their preferences and allows them to immerse themselves in their favorite subject matters.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, leaves play a crucial role in plants as they facilitate photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Leaves have a specific structure consisting of the blade, petiole, veins, cuticle, and stomata. While leaves are primarily involved in photosynthesis, they also have other functions such as transpiration and providing support for various plant structures.
Furthermore, not all plants have leaves, and some species have evolved different structures for photosynthesis. During the winter season, deciduous plants shed their leaves to conserve energy and reduce water loss. Overall, leaves are essential for the survival and growth of plants, and understanding their purpose helps us appreciate the intricate processes happening in the natural world.