Tomato plants, scientifically known as Solanum lycopersicum, are a popular choice for home gardeners due to their versatility and rich fruit yield. As these plants mature and grow, they require appropriate support and care to ensure optimal growth and fruit production. One crucial aspect to consider is the method of tying up tomato plants, which plays a vital role in preventing damage, promoting efficient growth, and maximizing the overall harvest. In order to achieve these goals, it is essential to explore the best practices to effectively tie up tomato plants. By understanding the various techniques and materials available, gardeners can provide the necessary support for their tomato plants, setting the stage for a flourishing and rewarding harvest.
key Takeaways
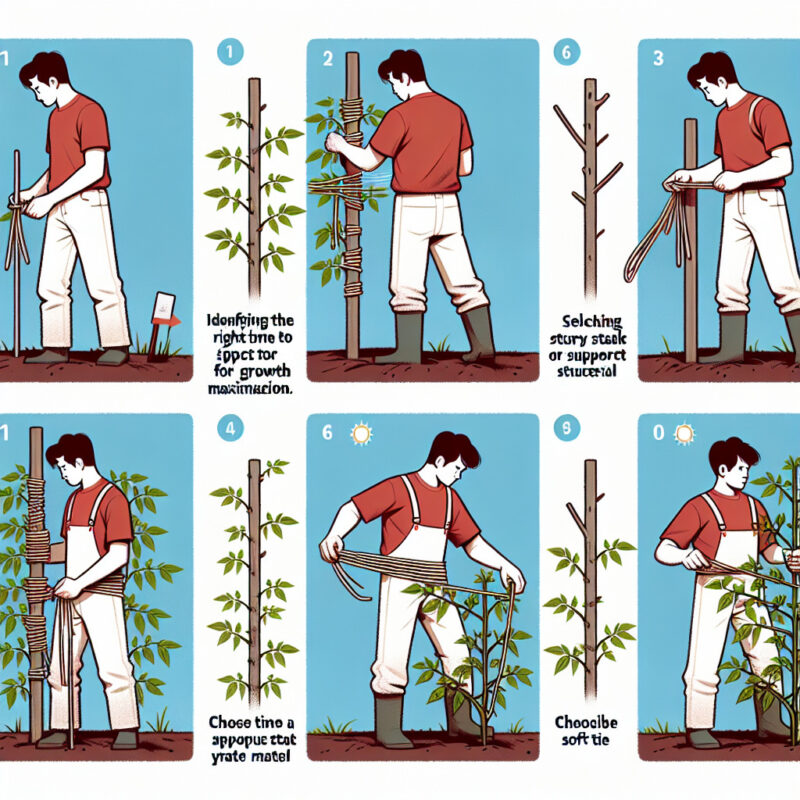
- Tomato plants need to be tied up to provide support as they grow and produce fruit.
- Tying up tomato plants helps prevent diseases and pests by keeping the foliage off the ground.
- Using a trellis or stakes are common methods of tying up tomato plants.
- When using stakes, it is important to drive them deep into the ground to ensure stability.
- Pruning tomato plants can help manage their growth and make them easier to tie up.
- Soft materials like strips of cloth or pantyhose should be used to tie up tomato plants, avoiding wire or twine that can damage the stems.
- Regularly check and adjust the ties as the tomato plants grow to prevent constriction or damage to the stems.
- Different tying techniques such as the figure-eight or spiral method can be used to secure tomato plants to their support system.
- Tying up tomato plants ensures better air circulation, sunlight exposure, and overall plant health.
- Properly securing tomato plants can maximize fruit production and make harvesting easier.
1. Introduction
Tying up tomato plants is an essential practice for promoting healthy growth, preventing damage, and maximizing productivity. Keeping the plants properly supported and upright allows for better air circulation, sunlight exposure, and efficient use of space. In this article, we will explore various techniques and materials to determine the best way to tie up tomato plants.
2. Tomato Plant Support
Tomato plants require support to prevent them from sprawling on the ground, which can lead to diseases and pests. The most common way to provide support is by using stakes, cages, or trellises. Stakes are vertical supports that are hammered into the ground next to the tomato plant. Cages are wire structures that surround the plant, offering multiple points of support. Trellises are frameworks, often made of wooden or metal posts with horizontal wires or strings for the plants to climb.
3. Types of Materials
When it comes to tying up tomato plants, choosing the right materials is crucial for effective support. Soft materials like gardening twine, string, or strips of fabric are commonly used as they are gentle on the plants’ stems. These materials allow flexibility for growth while maintaining stability. Plastic zip ties, while convenient, should be used with caution as they may constrict the stems as the plants get thicker. Natural materials such as jute or raffia can also be used, providing an organic and biodegradable option.
4. Techniques for Tying
There are various techniques for tying up tomato plants, and the choice depends on the support structure used. For staking, loosely tie the main stem to the stake at regular intervals using a figure-eight or spiral technique. This provides support while allowing room for growth. When using cages, gently pull the stems through the openings, ensuring they are supported and not constricted. With trellises, use clips or Velcro straps to secure the stems to the wires or strings. Regularly check and adjust the ties as the plants grow.
5. Pruning for Effective Tying
Pruning tomato plants is often necessary to manage their growth and facilitate tying. Remove any suckers or side shoots that emerge from the leaf axils, as they can divert energy from the main stem. Pruning also allows for better air circulation and reduces the risk of diseases. However, be mindful not to remove too much foliage, as the leaves are essential for photosynthesis.
6. Maintaining Tied Tomato Plants
As the tomato plants grow, regular maintenance of the ties is essential. Check the ties regularly to ensure they are not too tight, which can inhibit growth, or too loose, which can result in the plants toppling over. Adjust the ties as needed to provide continuous support. Moreover, keep an eye out for any signs of damage caused by the tying materials such as rubbing or girdling of the stems. Replacing or readjusting ties can prevent potential harm to the plants.
7. Conclusion
FAQs for “What Is The Best Way To Tie Up Tomato Plants”
1. Why is it important to tie up tomato plants?
Tying up tomato plants is essential for several reasons. First, it helps support the plants’ stems and branches, preventing them from breaking under the weight of the developing fruits. Additionally, tying up the plants creates better airflow around the foliage, reducing the risk of diseases such as fungal infections. Lastly, by tying up the tomato plants, you ensure that the fruits remain off the ground, minimizing the risk of rotting, pests, and diseases.
2. What are the different materials that can be used for tying up tomato plants?
There are various materials you can use to tie up tomato plants. Some popular options include soft twine, plant ties, garden twine, or strips of fabric. It’s important to choose materials that are durable, weather-resistant, and won’t damage the plants’ stems as they grow. Additionally, using materials that are easy to untie or adjust will help provide support as the plants continue to grow.
3. Is it necessary to tie up tomato plants from the start?
While it may not be necessary to tie up tomato plants when they are first transplanted, it is generally recommended to start supporting them once they reach a certain height. This could be around 6-8 inches in height or when the plants start developing branches. By providing support early on, you help prevent the plants from sprawling on the ground, which can increase the risk of diseases and pest infestations.
4. How should I tie up my tomato plants?
When tying up your tomato plants, it’s important to use a method that provides proper support and doesn’t damage the plants. A common technique is to use stakes or cages placed near the main stem of the plant and gently tie the branches to them using twine or plant ties. Make sure to tie the plant loosely, allowing room for growth but providing enough support to prevent breakage. It’s also important to regularly check and adjust the ties as the plants continue to grow.
5. Can I use tomato-specific cages instead of tying up tomato plants?
Absolutely! Tomato cages are a popular alternative to tying up tomato plants. These cages are typically made of metal or wire and provide structural support for the plants as they grow. They are easy to install, and the plants can naturally grow through the openings of the cage, giving them a sturdy framework to develop. However, it’s important to select appropriate-sized cages that can accommodate the growth of the plants and adequately support the weight of the fruits.
The Different Types and Options for Tomato Plant Supports
1. Stakes
One popular option for supporting tomato plants is using stakes. Stakes are usually made of wood, bamboo, or metal rods that are driven into the ground near the main stem of the plant. Plants can be gently tied to the stake, providing them with vertical support. Stakes are particularly useful for determinate varieties or bushier plants.
2. Tomato Cages
Tomato cages are another widely used support option. These cylindrical structures are made of either metal or wire and are placed around the plant at the time of transplanting. As the plants grow, they naturally weave through the openings of the cage, providing support to the branches and fruits. Tomato cages are suitable for both determinate and indeterminate varieties.
3. Trellis
A trellis is a vertical framework made of wood, metal, or even strings, onto which tomato plants can be trained to grow. Trellises offer good airflow, sunlight exposure, and support for the plants. They also help maximize space in smaller gardens. Indeterminate varieties, especially vining tomatoes, benefit the most from trellis systems.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, tying up tomato plants is crucial for their successful growth and development. It provides support to the stems and branches, improves airflow, and keeps the fruits off the ground. Popular materials for tying up tomato plants include twine, plant ties, and strips of fabric. While it may not be necessary to tie up tomato plants from the start, it is recommended to start supporting them once they reach a certain height or start developing branches.
When tying up tomato plants, it is important to use a gentle yet secure method, such as tying loosely with twine or using tomato cages. Stakes, cages, and trellises are common options for providing support to tomato plants. The choice of support method may depend on factors such as the tomato variety, the size of the plants, and the available gardening space. By properly tying up tomato plants, you can ensure healthier plants, better fruit production, and easier maintenance throughout the growing season.