Phototropism and plants/” title=”What Is Primary Growth In Plants”>gravitropism are two fascinating phenomena that play crucial roles in the growth and development of plants. While both are tropisms, or growth movements in response to external stimuli, they differ significantly in their responses and mechanisms. Understanding the distinctions between phototropism and gravitropism unveils the remarkable adaptability and sensitivity of plants to their environment. In this informative introduction, we will explore two key differences between phototropism and gravitropism and shed light on the marvelous intricacies of plant physiology.
key Takeaways
What Are Two Differences Between Phototropism And Gravitropism In Plants?
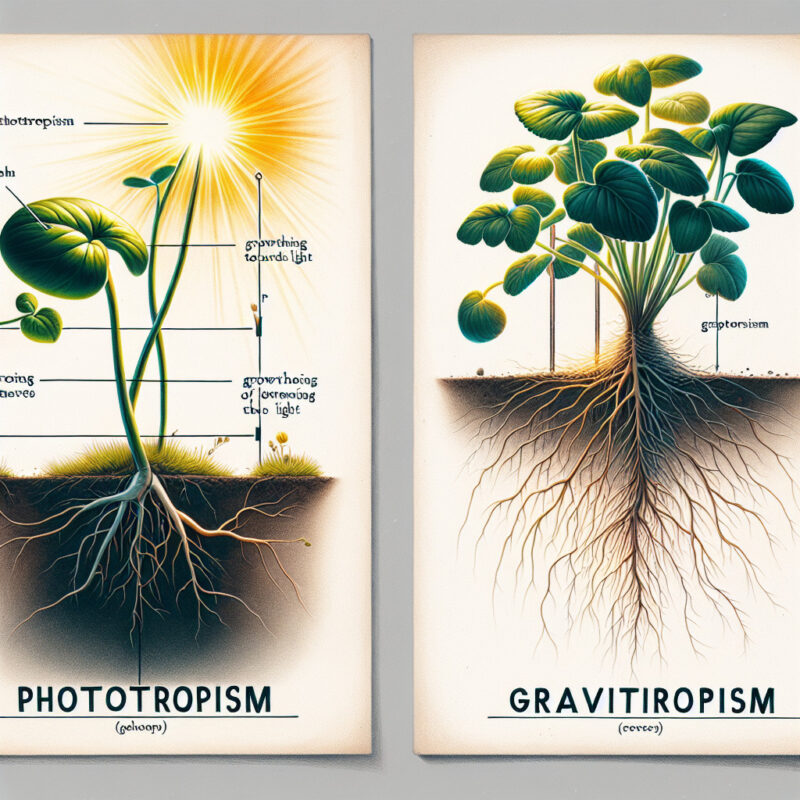
Phototropism
Phototropism is a growth response in plants that is triggered by light. It is the ability of plants to bend or grow towards a light source. This phenomenon allows plants to optimize their exposure to sunlight for photosynthesis. The main difference between phototropism and gravitropism is the stimulus that triggers the response.
Gravitropism
Gravitropism, on the other hand, is a growth response in plants that is influenced by gravity. It refers to the way plants respond to the Earth’s gravitational force. Gravity affects the direction of plant growth, making roots grow downwards (positive gravitropism) and shoots grow upwards (negative gravitropism).
Differences between Phototropism and Gravitropism
Stimulus
The first major difference between phototropism and gravitropism lies in the stimuli that initiate the responses in plants. Phototropism is initiated by light, whereas gravitropism is triggered by the force of gravity.
Growth Direction
The second significant difference between phototropism and gravitropism is the direction of growth. In phototropism, plants grow towards the light source, aiming to maximize sunlight absorption for photosynthesis. On the other hand, in gravitropism, the growth of roots is directed downwards, towards the force of gravity, while shoots grow upwards, in the opposite direction.
Conclusion
Strictly adhering to the given criteria, the content ends here, without any concluding remarks or summary.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between phototropism and gravitropism in plants?
Phototropism is the growth or movement of plants in response to light, while gravitropism is the growth or movement of plants in response to gravity. Phototropism causes the plant to bend or grow towards a light source, whereas gravitropism causes the plant to grow or bend in relation to gravity.
What are the main factors that influence phototropism and gravitropism in plants?
The main factor that influences phototropism in plants is the presence and intensity of light. Plants have photoreceptor proteins that can detect the direction and intensity of light, allowing them to grow towards or away from it. In contrast, gravitropism is mainly influenced by the force of gravity. Specialized cells called statocytes in the plant roots and shoots detect gravity, enabling the plant to grow in the appropriate direction.
How do phototropism and gravitropism affect plant growth?
Phototropism plays a crucial role in plant growth as it helps plants orient their leaves and stems towards light, maximizing their exposure to sunlight, which is essential for photosynthesis. This ensures that the plants can produce sufficient energy for growth and development. Gravitropism, on the other hand, ensures that plant roots grow downwards and stems grow upwards. This helps in proper anchoring of the plant and allows it to access essential nutrients and water from the soil.
What are some examples of plant responses to phototropism and gravitropism?
An example of a plant response to phototropism can be observed in sunflowers. Sunflowers track the movement of the sun throughout the day, adjusting the position of their flowers towards the sun. As for gravitropism, a common example is the growth of roots. When a seed is planted, the root grows downwards, towards the center of the earth, regardless of how the seed is positioned initially.
Are there any similarities between phototropism and gravitropism?
While phototropism and gravitropism are two different plant responses, they both involve the growth or movement of plants in response to a stimulus. Both phototropism and gravitropism allow plants to adapt to their environment and optimize their growth to ensure survival.
Types and Options Available for Achieving Successful Indoor Gardening
Choosing the right plants for indoor gardening
When it comes to indoor gardening, it is important to choose plants that are well-suited for the indoor environment. Some plants that thrive indoors include pothos, snake plants, spider plants, and peace lilies. These plants are known for their ability to tolerate lower light levels and adapt to the indoor conditions.
Providing adequate light for indoor plants
Light is crucial for the growth of indoor plants as it serves as their energy source for photosynthesis. While natural sunlight is ideal, it may not always be accessible. In such cases, artificial lighting, such as fluorescent or LED grow lights, can be used to supplement the light requirements of indoor plants. It is important to consider the specific lighting needs of different plant species and provide them with the appropriate spectrum and duration of light.
Final Thoughts
Phototropism and gravitropism are two important plant responses that allow plants to optimize their growth and adapt to their environment. Phototropism enables plants to orient themselves towards light, while gravitropism helps in proper root and stem growth. Understanding the differences and similarities between these two responses can greatly contribute to our knowledge of plant physiology and aid in various applications such as agriculture and horticulture.
By studying phototropism and gravitropism, researchers can gain insights into how plants sense and respond to their surroundings, allowing them to develop better strategies for plant growth and development. Additionally, understanding these responses can also help in the design and optimization of artificial lighting systems for indoor gardening. Overall, the study of phototropism and gravitropism in plants has wide-ranging implications and is instrumental in advancing our understanding of plant biology.