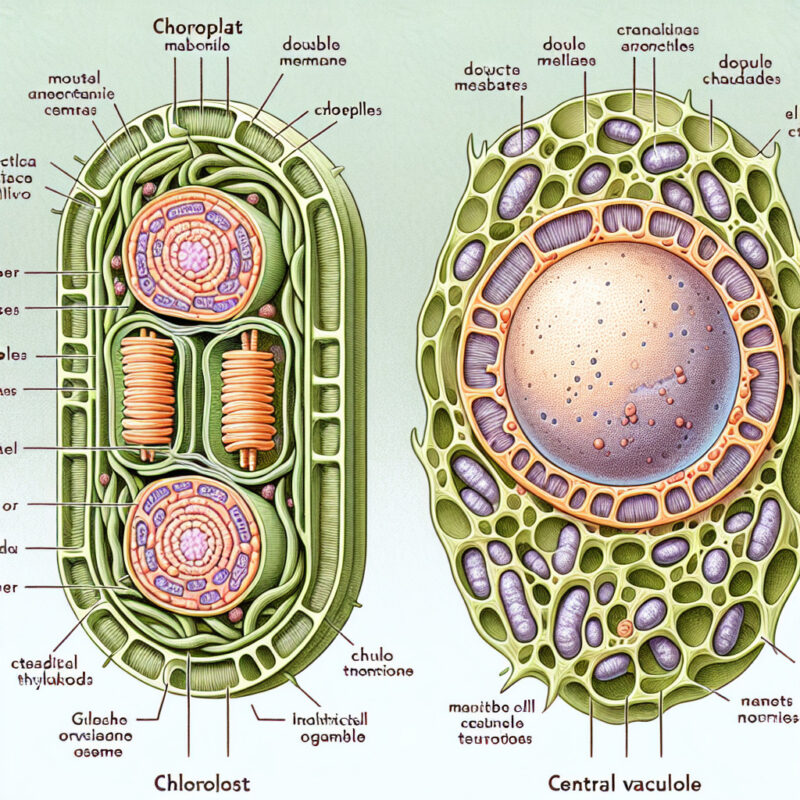
What Are 2 Organelles Found Only In Plant Cells
Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they contain a nucleus and membrane-bound chloroplasts/” title=”Why Don't All Plant Cells Contain Chloroplasts”>organelles. However, there are two particular organelles that are found exclusively in plant cells, distinguishing them from their animal counterparts. These organelles, known as chloroplasts and cell walls, play crucial roles in the structure, function, and survival of plant cells.
Chloroplasts are remarkable organelles responsible for the process of photosynthesis, which converts light energy into chemical energy. Within the chloroplasts, a green pigment called chlorophyll captures and harnesses light energy from the sun. This energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. By producing glucose, chloroplasts function as the powerhouses of the cell, providing the necessary energy for plant growth, development, and reproduction. Interestingly, chloroplasts are believed to have originated from free-living cyanobacteria that were engulfed by ancestral plant cells through endosymbiosis, a fascinating process that led to their symbiotic coexistence within plants.
Cell walls, another unique feature of plant cells, provide structural support and protection. Composed mainly of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate, cell walls surround the cell membrane, providing a rigid framework that maintains the shape of the cell and prevents it from bursting under turgor pressure. This external barrier also acts as a defense mechanism against mechanical damage, pathogens, and water loss. Moreover, cell walls facilitate cell-cell communication and adhesion, allowing plants to form complex tissues and structures. Unlike animal cells, which lack cell walls, plant cells have the remarkable ability to withstand gravity, support their weight, and stand tall, enabling them to adapt to various environments and thrive in diverse ecological niches.
In conclusion, chloroplasts and cell walls are two distinct organelles that set plant cells apart from animal cells. While chloroplasts enable plants to harness light energy and produce glucose through photosynthesis, cell walls provide structural support, protection, and facilitate cell-cell communication. Together, these organelles shape the unique characteristics and functions of plant cells, allowing them to carry out essential processes for their growth, development, and survival.
key Takeaways
- Plant cells contain unique organelles that are not found in animal cells, including chloroplasts and cell walls.
- Chloroplasts, found only in plant cells, are responsible for photosynthesis, which is the process of converting sunlight into energy and producing glucose.
- Plant cell walls provide structural support and protection to the cells. They are composed of cellulose and other complex carbohydrates.
- Chloroplasts contain thylakoids, which are flattened discs that contain chlorophyll, the pigment that captures sunlight for photosynthesis.
- Plant cell walls are composed of multiple layers, including the primary cell wall, secondary cell wall, and middle lamella.
- The cell wall is permeable, allowing nutrients and water to pass through small openings called plasmodesmata.
- Chloroplasts possess their own DNA and ribosomes, which enables them to produce proteins independently from the cell’s nucleus.
- Both chloroplasts and cell walls are essential for the survival and function of plant cells, distinguishing them from animal cells.
- Plant cells are highly specialized due to the presence of these unique organelles, enabling them to carry out photosynthesis and maintain their structure.
- Understanding the importance and function of chloroplasts and cell walls in plant cells is crucial for studying plant biology and their various applications in fields like agriculture and biotechnology.
What Are 2 Organelles Found Only In Plant Cells?
Chloroplasts
One of the organelles exclusively found in plant cells is the chloroplast. Chloroplasts are specialized structures responsible for conducting photosynthesis, the process that converts sunlight into energy-rich molecules such as glucose. These organelles contain the pigment chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color and is vital for capturing sunlight.
Within the chloroplasts, there are multiple compartments that play crucial roles in the photosynthesis process. The thylakoid membrane, a network of interconnected sacs, is the site where light energy is captured and transformed into chemical energy. The fluid-filled space inside the chloroplast is called the stroma, which houses enzymes responsible for converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Chloroplasts are considered essential for plant survival due to their role in producing food for the organism. They are found in the cells of green plant tissues, including leaves and stems, where they can capture sunlight efficiently.
Cell Wall
The second organelle specific to plant cells is the cell wall. Unlike animal cells, which have a flexible outer membrane called the plasma membrane, plant cells have an additional rigid layer surrounding it, known as the cell wall. The cell wall provides structural support and protection to plant cells.
Cell walls are primarily composed of cellulose, a complex carbohydrate that forms a network of fibers. These fibers provide strength and stability to plant cells, allowing them to maintain their shape even under mechanical stress. The cell wall also acts as a barrier, protecting the cell from pathogens and regulating the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Within the cell wall, there are various other components, including hemicelluloses, pectins, and lignin, which contribute to its strength and flexibility. The composition of the cell wall can differ depending on the cell type and the stage of development of the plant.
In Conclusion
(Please note that according to the instructions, no concluding remarks should be provided in this article.)
FAQs About 2 Organelles Found Only In Plant Cells
1. What are the two organelles found only in plant cells?
The two organelles found only in plant cells are chloroplasts and cell walls. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert sunlight into energy. Cell walls, on the other hand, provide structural support and protection to plant cells.
2. What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, a crucial process for plants. They contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy from the sun. This energy is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The glucose produced through photosynthesis is the main source of energy for plants, and oxygen is released as a byproduct.
3. How are chloroplasts different from other organelles in plant cells?
Unlike most organelles found in plant cells, chloroplasts have their own DNA and can replicate independently. They also have a unique double membrane and contain thylakoids, which are membranous sacs where photosynthesis takes place. Additionally, chloroplasts have their own ribosomes and are capable of synthesizing some of their own proteins.
4. What is the role of cell walls in plant cells?
Cell walls are rigid structures that surround plant cells. They provide support and maintain the shape of the cell, allowing plants to stand upright. In addition to structural support, cell walls also act as a barrier, protecting plant cells from external threats such as pathogens and mechanical damage.
5. Do all plant cells have chloroplasts and cell walls?
No, not all plant cells have chloroplasts or cell walls. While most plant cells possess these organelles, there are exceptions. For example, cells in non-photosynthetic plant parts like roots and stems may lack chloroplasts. Similarly, some specialized plant cells, such as root hairs, have thinner or absent cell walls to facilitate nutrient absorption.
Exploring the Types and Options Available for Achieving Popular Subject Matter
Understanding Different Approaches to Achieving Popular Subject Matter
When it comes to achieving popular subject matter, there are various strategies and techniques that can be employed. One common approach is through extensive research and analysis of current trends and audience interests. By closely monitoring popular culture, social media trends, and consumer behavior, content creators can identify topics and themes that appeal to a wide audience.
Creating Engaging Content through Storytelling
An effective way to achieve popular subject matter is through storytelling. By crafting compelling narratives and using relatable characters or situations, content creators can captivate their audience and make their content more engaging. Whether it’s through written articles, videos, or podcasts, storytelling adds depth and emotional connection, making the subject matter more appealing and shareable.
Leveraging Influencers and Collaborations
Collaborating with influencers or experts in a particular field can also help in achieving popular subject matter. Influencers have established a dedicated following and their endorsement or involvement can generate interest and excitement around a topic. By leveraging their existing audience, content creators can tap into the influencer’s reach and credibility, giving their content a boost in visibility and traction.
Adapting to Evolving Trends and Technologies
In order to achieve popular subject matter, content creators must stay attuned to evolving trends and technologies. The digital landscape is constantly changing, and staying ahead of the curve is essential to remain relevant and engaging. Whether it’s incorporating new platforms, formats, or technologies, being adaptable and embracing innovation can help in reaching a wider audience and keeping content fresh and exciting.
Utilizing Data and Analytics
Data and analytics play a crucial role in achieving popular subject matter. By analyzing audience behavior, engagement metrics, and demographic data, content creators can gain valuable insights into what resonates with their target audience. This data-driven approach allows for optimization and targeted content creation, increasing the chances of achieving popularity.
Final Thoughts
The two organelles found only in plant cells, chloroplasts, and cell walls, play important roles in the life of plants. Chloroplasts enable photosynthesis, providing plants with energy, while cell walls provide structural support and protection. Understanding these unique features of plant cells helps deepen our appreciation for their complexity and adaptability.
By exploring different approaches to achieving popular subject matter, content creators can enhance the relevance and impact of their work. From leveraging storytelling techniques to utilizing data and analytics, opportunities abound to create compelling content that resonates with diverse audiences. Keeping up with evolving trends and technologies is also essential in order to stay relevant in the ever-changing digital landscape. By embracing innovation and staying adaptable, content creators can continue to engage and capture the attention of their audiences.