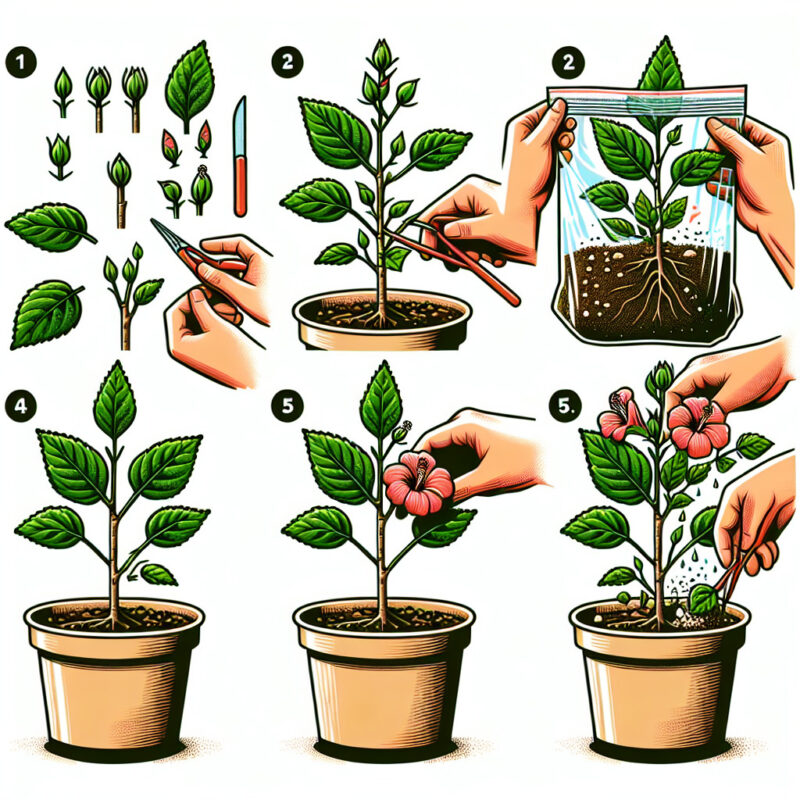
Hibiscus plants are a beautiful addition to any garden or indoor space. If you’ve ever wanted to grow more of these stunning flowers, propagating your hibiscus plant is a great way to do so. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the simple steps of propagating hibiscus, so you can enjoy more of these vibrant blooms in your home.
First, let’s start with the supplies you’ll need. To propagate your hibiscus plant, you’ll need a sharp and clean pair of pruning shears, a clean container filled with well-draining potting soil, and some rooting hormone. These materials will ensure a successful propagation process.
Begin by selecting a healthy branch from your existing hibiscus plant. Look for a young shoot with at least three to four leaves. Using your pruning shears, make a clean and angled cut about four to six inches below the leaf node. The leaf node is the point on the stem where the leaves emerge.
Once you’ve made the cutting, remove any lower leaves so that only the uppermost leaves remain on the stem. This will allow the energy to be directed towards root growth. Dip the cut end of the stem into rooting hormone powder, which will encourage root development.
Next, prepare your container filled with well-draining potting soil. Make a small hole in the soil using your finger or a pencil, about two inches deep. Gently place the cutting into the hole, making sure it stands upright. Press the soil around the stem to secure it in place.
After planting, water the cutting thoroughly until you see water draining out from the bottom of the container. This will ensure that the soil is evenly moist. Place your container in a warm and bright location but avoid direct sunlight, as it may be too intense for the young cutting.
Over the next few weeks, keep an eye on the soil moisture and water whenever it feels slightly dry. You should start to see new growth emerging from the cutting within a month or so. Once the cutting has developed a strong root system and several new leaves, it is ready to be transplanted into a larger pot or directly into your garden.
Remember to be patient and give your cutting time to establish itself. It may take several months for the new plant to grow to a substantial size. With proper care and attention, your propagated hibiscus plant will eventually reward you with a multitude of vibrant and eye-catching flowers. Enjoy the process and the satisfaction of growing your own hibiscus plants!
Preparing the Cutting
Choose a healthy hibiscus plant with strong stems and vibrant leaves. Use sharp pruning shears to cut a 4-6 inch section from the tip of a stem just below a leaf node. Remove any lower leaves from the cutting, leaving 2-3 leaves at the top. Dip the cut end in rooting hormone powder to promote root growth.
Planting the Cutting
Fill a small pot with well-draining potting mix. Make a hole in the soil using a pencil or your finger and gently place the cutting into the hole. Firmly press the soil around the base of the cutting to ensure good contact. Water the cutting thoroughly but avoid oversaturation.
Providing Optimal Growing Conditions
Place the potted cutting in a warm, bright location away from direct sunlight. Maintain a temperature of around 70-80°F (21-27°C). Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged, watering whenever the top inch of soil feels dry. Use a misting bottle to lightly mist the leaves daily for increased humidity.
Encouraging Root Growth
Cover the potted cutting with a clear plastic bag or a glass jar to create a mini greenhouse effect. This will help retain moisture and create a humid environment conducive for root development. Make sure to ventilate occasionally to prevent excess moisture buildup.
Transferring to a Larger Pot
After 6-8 weeks, gently tug the cutting to check for resistance, indicating root growth. Once roots have formed, carefully transplant the cutting into a larger pot with well-draining soil. Choose a pot that allows for sufficient root growth and drainage. Water thoroughly after transplanting and continue to provide optimal growing conditions as before.
Monitoring and Care
Monitor the newly propagated hibiscus plant closely for signs of stress or drying out. Ensure it receives bright, indirect sunlight and maintain a consistent watering schedule. Fertilize regularly with a balanced liquid fertilizer during the growing season. Prune as necessary to shape the plant and promote bushier growth. With proper care, your hibiscus plant will thrive and bring you beautiful blooms.
Pros of How To Propagate Hibiscus Plant
- Cost-effective: Propagating hibiscus plants is a cost-effective way to expand your garden. Instead of purchasing new plants, you can propagate from existing ones, saving money on buying new plants.
- High success rate: Propagating hibiscus plants is relatively easy, and they have a high success rate. With the right techniques and care, you can expect a high percentage of successful propagation, resulting in more beautiful hibiscus plants.
- Increased plant supply: Propagation allows you to increase your hibiscus plant supply. By propagating them, you can create new plants that can be used to fill empty spots in your garden or shared with friends and family.
- Genetic preservation: Propagating hibiscus plants allows you to preserve specific genetic traits that you admire in your existing plants. By propagating from these plants, you can ensure the continuation of their unique characteristics in future generations.
- Learning opportunity: Propagation is a great learning opportunity for gardeners of all levels. It allows you to understand the plant’s reproductive cycle, experiment with different techniques, and develop your skills in plant propagation.
- Plant customization: Propagating hibiscus plants gives you the opportunity to create unique variations. Through cross-pollination and selective breeding, you can develop new color variations or plant forms that are not commonly found in nurseries.
For example, suppose you have a beautiful hibiscus plant with vibrant red flowers. By propagating it, you can create several new plants with the same captivating red flowers, expanding the presence of this stunning color in your garden. Additionally, you can cross-pollinate different hibiscus plants with unique colors, resulting in a new plant variety that combines the best traits of both parents.
Cons of How To Propagate Hibiscus Plant
- Time-consuming process: Propagating hibiscus plants can be a lengthy procedure that requires patience. It involves multiple steps, such as collecting and preparing cuttings, rooting them, and then caring for the new plants until they are established. This can discourage individuals who are looking for quick results or lack the necessary time commitment.
- Higher failure rate: Successfully propagating hibiscus plants is not guaranteed, and there is a possibility of failure. This can be due to various factors, including inadequate rooting conditions, improper care, or pest infestations. It can be disheartening to invest time and effort into propagating plants only to see them wither or fail to grow.
- Risks of disease transmission: When propagating hibiscus plants, there is a risk of introducing diseases or pests to the new plants. If the parent plant has any underlying health issues, those problems can be passed on to the propagated plants, making them vulnerable to diseases or causing stunted growth. This can potentially lead to a negative cycle where multiple plants are affected.
- Requirement for specific environmental conditions: Hibiscus plants have specific environmental needs to thrive, and this applies to both parent plants and propagated ones. Factors such as temperature, humidity, sunlight, and soil quality play a crucial role in the success of propagating hibiscus plants. If these conditions are not met adequately, it can hinder the growth and development of the propagated plants.
- Limited genetic diversity: When propagating hibiscus plants, the resulting new plants are essentially clones of the parent plant. This lack of genetic diversity can make the propagated plants susceptible to the same pests and diseases as the parent plant, limiting their ability to adapt to changing environmental conditions or resist certain threats.
One instance where the time-consuming nature of propagating hibiscus plants becomes apparent is when rooting cuttings. It can take several weeks for the root systems to develop, and during this time, the cuttings require regular watering and monitoring. Any neglect or improper care can hinder root formation, leading to unsuccessful propagation.
In a case study, a gardener attempted to propagate hibiscus plants from cuttings but encountered a high failure rate. Despite following the proper procedures, many of the cuttings failed to root or died shortly after. This highlighted the challenge and uncertainty associated with successfully propagating hibiscus plants, even for experienced individuals.
Another drawback of propagating hibiscus plants is the risk of disease transmission. In a particular instance, a propagated hibiscus plant showed signs of leaf yellowing and wilting. Upon examination, it was found that the plant had inherited a fungal infection from the parent plant, which ultimately led to its demise. This highlights the potential consequences of propagating plants from a parent with existing health issues.
Overall, while How To Propagate Hibiscus Plant offers the potential for expanding hibiscus populations, it comes with its share of drawbacks. The time-consuming process, higher failure rate, risks of disease transmission, specific environmental requirements, and limited genetic diversity all pose challenges and considerations for those interested in propagating these plants.