Air plants, also known as Tillandsia, are unique and fascinating plants that have captured the attention of many indoor gardening enthusiasts. Unlike traditional plants that require soil to grow, air plants absorb nutrients and moisture from the air, making them easy to care for and maintain. This ability to thrive without soil has made them a popular choice for anyone looking to add some greenery to their living spaces. In addition to their low-maintenance requirements, air plants also offer a wide range of creative and decorative possibilities. From hanging them in glass terrariums to mounting them on driftwood or creating living walls, the possibilities are endless.
Now that we have established the intriguing nature of air plants, let’s dive into the key takeaways when it comes to propagating these unique plants. Understanding the process of propagation is essential if you want to expand your air plant collection or share your passion for these remarkable plants with others. In the following sections, we will explore the different methods of propagating air plants, including division, offsets, and seed germination. We will also discuss the best practices for each method and provide helpful tips to ensure success. So, whether you are new to air plants or a seasoned enthusiast, read on to discover the secrets of propagating air plants and watch your collection thrive.
Key Takeaways
1. Air plants can be easily propagated through several methods, including division, offsets, and seed germination.
2. Removing offsets from the parent plant and allowing them to grow on their own is a simple and effective method of propagation.
3. Proper care and maintenance of air plants are essential for successful propagation, including providing adequate light, misting or soaking them in water regularly, and ensuring good air circulation.
4. Seed germination is a more challenging but rewarding method of propagating air plants, requiring specific conditions such as temperature control and a moist environment.
5. Patience is key when propagating air plants as it may take several months or even years for new plants to reach maturity, but with the right care and techniques, a thriving collection can be achieved.
How can you propagate an air plant?
What is an air plant?
An air plant, also known as Tillandsia, is a type of plant that doesn’t require soil to grow. It belongs to the Bromeliad family and is a popular choice among plant enthusiasts due to its unique appearance and minimal care requirements.
Why propagate air plants?
Propagating air plants is a great way to expand your plant collection and share the beauty of these fascinating plants with others. It allows you to grow new plants from the parent plant, making it a cost-effective method to obtain more air plants.
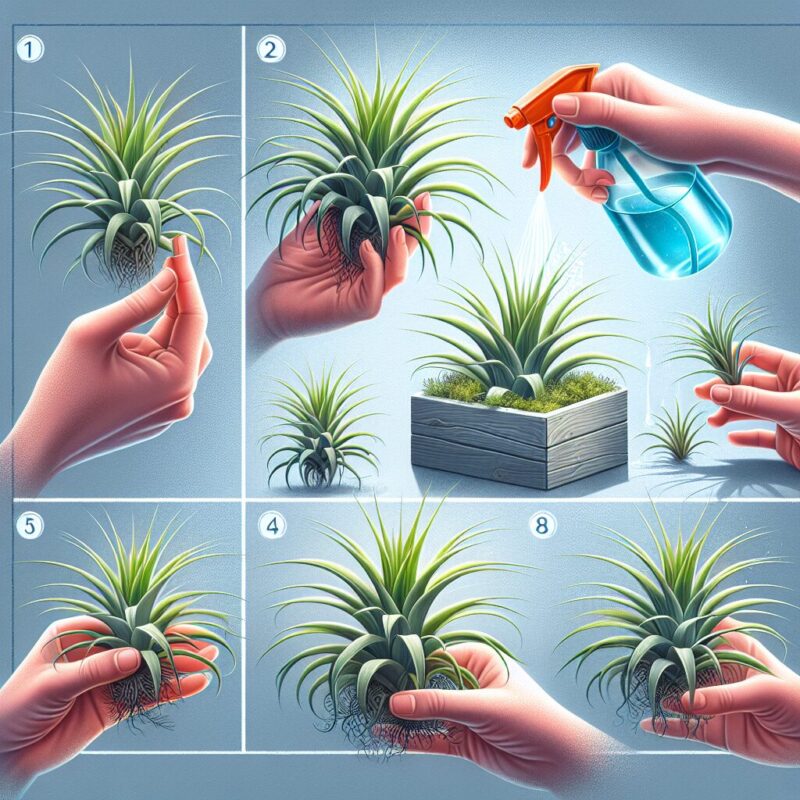
Methods of air plant propagation
There are various methods you can use to propagate air plants, including:
1. Division
Division is one of the simplest and most common methods of propagating air plants. Here’s how you can do it:
- Gently remove the air plant from its container.
- Inspect the plant for any natural separations or offshoots, known as “pups.”
- With clean, sharp scissors, carefully separate the pup from the parent plant by cutting the connecting tissue.
- Ensure that the pup has some root structure attached.
- Plant the pup in a suitable growing medium or attach it to a new surface using glue or wire.
- Provide appropriate care to the newly propagated air plant, including regular misting and indirect light.
2. Seed sowing
Another method to propagate air plants is through seed sowing, although it is less commonly practiced due to the slow growth rate of air plant seeds. Nevertheless, if you wish to try this method, follow these steps:
- Obtain air plant seeds from a reliable source.
- Prepare a well-draining potting mix suitable for air plants.
- Sow the air plant seeds on top of the potting mix and gently press them down.
- Keep the seeds consistently moist and maintain a warm temperature.
- Be patient, as air plant seeds can take several weeks or even months to germinate.
- Once the seedlings have grown, provide the same care as mature air plants.
3. Offsets or pups
Air plants naturally produce offsets or pups as a form of reproduction. These small plants grow alongside the parent plant and can be separated and grown independently. Follow these steps to propagate air plants using offshoots:
- Gently remove the pup from the parent plant.
- Ensure that the pup has some root structure attached.
- Place the pup in a suitable growing medium or attach it to a new surface using glue or wire.
- Provide appropriate care to the newly propagated air plant, including regular misting and indirect light.
Tips for successful air plant propagation
- Ensure the parent plant is healthy and mature before attempting to propagate.
- Use clean and sharp tools to prevent damage to the plants.
- Provide proper humidity and air circulation to aid in the development of new plants.
- Avoid direct sunlight, as it can cause damage to the delicate air plant pups.
- Regularly mist or soak the newly propagated plants to maintain proper hydration.
1. Can air plants be propagated from seeds?
No, air plants cannot be propagated from seeds. Instead, they reproduce by producing offsets or pups which can be separated from the parent plant.
2. How do I know when my air plants are ready to be propagated?
Air plants are ready to be propagated when they start producing new offsets or pups. This usually occurs after the parent plant has bloomed.
3. What is the best method to propagate air plants?
The best method to propagate air plants is by gently removing the offsets or pups from the parent plant and allowing them to establish roots on their own. This can be done by gently pulling them apart or using a clean, sharp knife to separate them.
4. How long does it take for the propagated air plants to establish roots?
It generally takes around 2-4 weeks for the propagated air plants to establish roots. During this time, it is important to provide them with adequate moisture and light to ensure successful rooting.
5. Can I propagate air plants in water?
While it is possible to propagate air plants in water, it is not the preferred method as it can lead to rot and damage to the plant. It is best to let the plants establish roots in a suitable growing medium.
6. How often should I water the newly propagated air plants?
The newly propagated air plants should be misted or soaked in water once or twice a week, depending on the environmental conditions. It is important not to overwater them as it can lead to root rot.
7. Do I need to fertilize the propagated air plants?
Air plants do not require frequent fertilization. However, a diluted, balanced fertilizer can be used sparingly once every one to three months to provide them with essential nutrients.
8. Can air plants be propagated by division?
Air plants can be propagated by division. This involves separating a clump of air plants into individual plants, ensuring each has some roots attached. This method can be used when the plant has formed a dense cluster.
9. How long does it take for the propagated air plants to reach maturity?
The time it takes for the propagated air plants to reach maturity varies depending on various factors such as the species and growing conditions. Generally, it can take several months to a year for the newly propagated plants to fully mature.
10. Can I propagate air plants from cuttings?
No, air plants cannot be propagated from cuttings. They only reproduce through offsets or pups that are produced by the parent plant.
Final Thoughts on How To Propagate Air Plant:
Propagation of air plants can be a rewarding and enjoyable experience for any plant enthusiast. By following the proper techniques and providing the necessary care, you can successfully multiply your air plant collection and create a stunning display. Remember to be patient, as the process may take time, but the results are well worth it. Happy propagating!