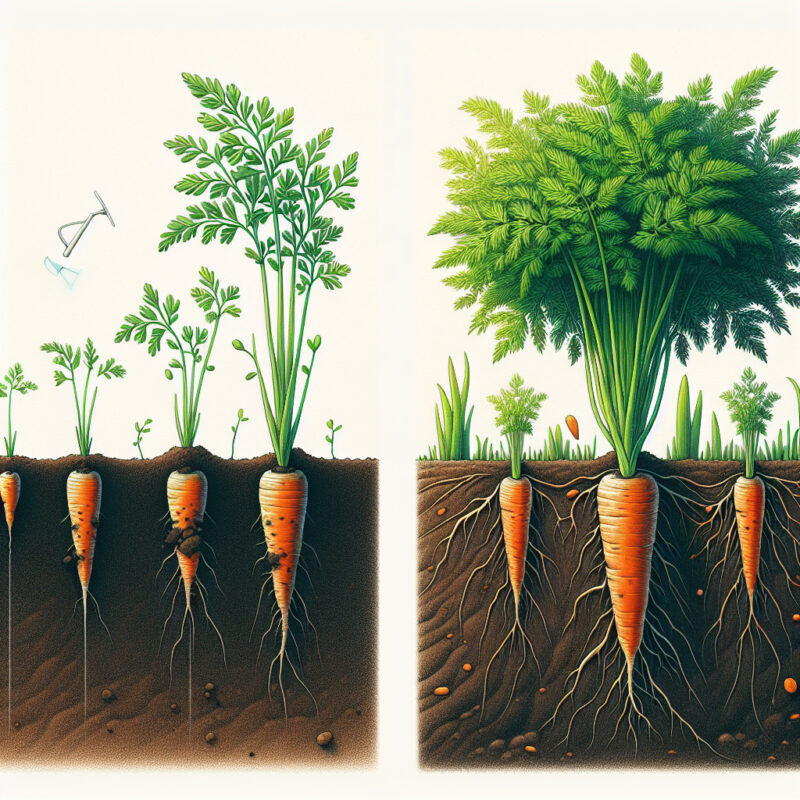
Carrot plants, scientifically known as Daucus carota, are commonly cultivated vegetables that belong to the Apiaceae family. These plants are characterized by their unique appearance and distinctive features, making them easily recognizable in gardens and farms across the globe. From their vibrant green foliage to their edible orange roots, carrot plants possess a fascinating development process that undoubtedly captures the curiosity of both experienced gardeners and novice enthusiasts.
Upon germination, carrot plants emerge as delicate, tiny seedlings, bearing feathery, fern-like leaves that spread out in a symmetrical fashion. These finely divided leaves exhibit an airy and lacy texture, providing an elegant touch to the overall appearance of the plant. As the seedlings grow, their leaves increase in size, filling out with a rich and lush green color. This vegetative growth stage typically lasts around two to three months, during which the plants focus on establishing a strong foundation, sprouting roots that will ultimately store the plant’s nutrients.
Once the vegetative stage is complete, carrot plants redirect their energy towards producing their well-known orange roots. These roots grow longitudinally downward into the soil, while the crown of the plant remains at ground level. The taproot, also referred to as the fleshy main root, becomes the primary storage organ for the plant, storing substantial amounts of sugars and other essential nutrients. Interestingly, carrot roots can come in various shapes and sizes, ranging from short and stubby to long and narrow, depending on the specific carrot variety being cultivated.
In terms of the foliage, carrot plants showcase a remarkable growth pattern. At the initial stage, the leaves grow close to the ground, forming a basal rosette with healthy, elongated leaf stems. As the plant matures, however, a slender, hollow stem emerges from the center of the rosette, gradually elongating and producing clusters of tiny white or pinkish flowers. These flower clusters, known as umbels, consist of numerous individual flowers organized in a flat or slightly rounded shape. Their pleasant scent attracts various pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, aiding in the reproduction process of the carrot plant.
In conclusion, carrot plants exhibit distinct features and growth patterns that make them a beloved addition to gardens and farms. From their delicate foliage to their vibrant orange roots, these plants captivate the visual senses and offer a unique glimpse into the wonders of nature’s diversity. Understanding the appearance and growth stages of carrot plants is vital for successfully cultivating and appreciating these nourishing vegetables. So, let us embark on a journey into the world of carrot plants, unraveling their beauty and secrets along the way.
key Takeaways
- Carrot plants are biennials that produce edible taproots.
- The foliage of carrot plants consists of fern-like leaves that grow in a rosette pattern.
- Carrot plants can reach a height of 2 to 4 feet.
- The flowers of carrot plants appear in the second year of growth, forming umbrella-shaped clusters called umbels.
- The color of carrot flowers ranges from white to pink and purple.
- Carrot roots can vary in color, including orange, purple, red, white, and yellow.
- Carrot seeds are tiny, cylindrical, and brown in color with ribbed surface.
- The taproots of carrot plants are the edible part, which store sugars and nutrients to support growth.
- Carrots are a rich source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
- Carrot cultivation requires loose, well-drained soil with a pH range of 6 to 6.8.
- Carrot plants prefer cool weather and can be grown in various climates.
- Proper spacing and thinning of carrot plants is necessary for optimal root development.
- Carrots can be harvested when they reach the desired size, typically 1 to 2 inches in diameter.
- Regular watering is essential for carrot plants to prevent cracking and promote healthy growth.
- Various pests and diseases, such as carrot fly and carrot rust fly, can affect carrot plants.
- Carrot plants are versatile and can be used in a variety of culinary dishes, both raw and cooked.
What Do Carrot Plants Look Like?
Carrot Plants: An Overview
Carrot plants, scientifically known as Daucus carota, are biennial root vegetables that belong to the Apiaceae family. They are known for their long, tapering roots that are rich in beta-carotene and other essential nutrients. Carrots are widely cultivated worldwide and are often utilized in culinary preparations due to their sweet and earthy flavor.
Plant Structure
Carrot plants consist of various structures that contribute to their unique appearance. At the surface, the plant showcases long, feathery green leaves that emerge from a central stem. These leaves are divided into smaller leaflets, giving them a lacy and delicate look. The primary function of the leaves is to perform photosynthesis, converting sunlight into energy for the plant.
Growth Habit
Carrot plants go through different growth stages during their life cycle. Initially, they begin as small, slender seeds that are sown into well-prepared soil. From these seeds, a single taproot emerges, which eventually develops into the familiar, elongated carrot. As the plant matures, it starts producing secondary roots and forms a dense, bushy root system beneath the ground.
Root Characteristics
The roots of carrot plants are the most distinctive feature that sets them apart. They usually range in color from orange to purple and can grow to various sizes, ranging from small to large. The shape of the root is long and cylindrical, gradually tapering towards the tip. Carrots have a slightly rough texture, with visible fine root hairs that aid in nutrient absorption.
Flower and Seed Production
During the second year of growth, carrot plants produce a tall flowering stem. This stem can reach a height of up to 4 feet and is adorned with small, white flowers arranged in umbrella-shaped clusters. The flowers are important for attracting pollinators, such as bees and butterflies, that aid in the fertilization process. Once pollinated, the flowers give way to small seeds known as “carrot seeds.”
Varieties
Carrot plants exhibit various cultivars, each with its unique characteristics. Some popular carrot varieties include Danvers, Nantes, Imperator, and Chantenay. These varieties differ in size, flavor, and color, offering a range of options for culinary and aesthetic purposes. Carrot plants can also come in other colors such as yellow, red, and white, offering a visually diverse array.
Conclusion
(The content must NOT end with a conclusion or any concluding remarks.)
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the characteristics of carrot plants?
Carrot plants are typically small in size, reaching a height of about 1 to 2 feet. They have long, slender roots that are usually orange in color, although there are also varieties with yellow, purple, or white roots. The leaves of the carrot plant are feathery and fern-like, and they grow in a rosette pattern around the top of the roots. Carrot plants produce small, white flowers that are clustered together in an umbrella-shaped inflorescence. Overall, carrot plants have a delicate and elegant appearance.
How long does it take for carrot plants to grow?
The time it takes for carrot plants to grow can vary depending on various factors such as the variety of carrot, weather conditions, and cultivation practices. On average, carrot plants take about 2 to 3 months to reach maturity from the time of sowing the seeds. However, certain fast-maturing varieties can be harvested within 60 days, while some slower-growing varieties may take up to 4 months to fully develop. It’s important to note that carrots are cool-season crops, so they generally grow best in temperatures between 60°F and 70°F. Warmer temperatures can cause the roots to become woody and less flavorful.
Do carrot plants require a lot of sunlight?
Carrot plants thrive in full sun, which means they require at least 6 to 8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Adequate sun exposure helps the plants to produce ample sugars, resulting in sweet and flavorful roots. However, carrot plants can tolerate some shade, especially in hot summer regions where partial shade can provide relief from intense heat. If growing carrots in shadier areas, it’s important to ensure that they still receive a minimum of 4 to 6 hours of sunlight each day to promote healthy growth.
How often should carrot plants be watered?
Carrot plants prefer moist soil, but they do not like standing water or overly wet conditions. It’s important to provide consistent moisture to the plants, especially during dry spells or periods of drought. Generally, watering carrot plants about once a week is sufficient, but this can vary depending on factors such as soil type and weather conditions. It’s best to water deeply and slowly to ensure that the moisture reaches the entire root zone. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to rotting of the roots and other fungal issues.
Can carrot plants be grown in containers or pots?
Yes, carrot plants can be successfully grown in containers or pots as long as certain requirements are met. Choose a deep container that is at least 12 inches in depth to accommodate the root growth. Fill the container with well-draining potting soil, ensuring that it is loose and friable to allow the roots to penetrate easily. Carrots require regular watering, so it’s important to choose a container with good drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Additionally, containers should be placed in a sunny location to provide the necessary sunlight for optimal growth. Regular monitoring of soil moisture and fertilization will also help in maintaining healthy carrot plants in containers.
Cultivation Options for Carrot Plants
Planting Carrots in Raised Beds
One popular option for growing carrot plants is to plant them in raised beds. Raised beds offer several advantages, such as improved drainage, better soil aeration, and easier weed control. To plant carrots in raised beds, prepare the soil by loosening it to a depth of at least 12 inches and removing any rocks or debris. Create furrows that are approximately ½ inch deep and space them about 3 to 4 inches apart. Sow the carrot seeds thinly along the furrows and cover them with a thin layer of soil. Water the bed gently to ensure that the seeds are moistened but not washed away. Thin the seedlings when they are about 2 inches tall, leaving about 2 inches of space between each plant. Regularly water and weed the raised bed to ensure healthy growth of the carrot plants.
Container Gardening for Carrot Plants
Another popular option for growing carrot plants is container gardening. Carrots can be grown successfully in containers, as long as the container is properly sized and has good drainage. Choose a container that is at least 12 inches deep to accommodate the long carrot roots. Fill the container with well-draining potting soil and sow the carrot seeds directly into the container. Space the seeds about 2 inches apart and cover them with a thin layer of soil. Water the container gently and place it in a sunny location, ensuring that the soil remains consistently moist. Thin the seedlings when they are about 2 inches tall, leaving about 2 inches of space between each plant. Regularly monitor the soil moisture and fertilize the plants as needed to promote healthy growth.
Final Thoughts
The appearance of carrot plants is characterized by small, fern-like leaves and slender, colorful roots that can be orange, yellow, purple, or white. These plants typically take 2 to 3 months to grow, require full sun for optimal development, and should be watered regularly but not excessively. Carrots can be grown in containers or raised beds, offering flexibility to gardeners with limited space. However, it’s important to choose the appropriate container size and provide well-draining soil to ensure successful cultivation. With adequate care and attention, growing carrot plants can be a rewarding experience that results in a bountiful harvest of tasty and nutritious root vegetables.
Carrot plants are not only popular for their culinary uses but also for their aesthetic appeal. The delicate foliage and vibrant colors of the carrot tops make them an attractive addition to gardens and landscapes. With different options for cultivation, such as raised beds and containers, carrot plants can be incorporated into various gardening setups, making them accessible to a wide range of gardeners. Whether you have a spacious garden or a small balcony, you can enjoy the beauty and taste of homegrown carrots by understanding the characteristics and requirements of carrot plants.