Photosynthesis is a vital process that sustains the very essence of life on our planet. It is the remarkable ability of plants to convert sunlight into chemical energy, fulfilling their own energy needs while simultaneously producing the oxygen that all living organisms depend on. However, this fascinating phenomenon requires a precise combination of raw materials to occur. In this article, we will delve into the essential elements a plant needs for photosynthesis, shedding light on the intricate interplay between these components that enable plants to thrive and flourish.
key Takeaways
- Plants require several raw materials for photosynthesis to occur.
- The primary raw material for photosynthesis is carbon dioxide, obtained from the air through tiny pores called stomata.
- Water is another crucial raw material, taken up by plants from the soil through their roots.
- Light is an essential energy source for photosynthesis, as it provides the energy needed to convert raw materials into glucose.
- Chlorophyll, a pigment present in chloroplasts, captures light energy and initiates the process of photosynthesis.
- Additional raw materials required for photosynthesis include minerals such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and magnesium.
- Oxygen is produced as a byproduct of photosynthesis and is released into the atmosphere.
- The process of photosynthesis enables plants to convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose, which fuels plant growth and provides energy for other organisms.
- Photosynthesis plays a vital role in the Earth’s ecosystem, as it is the primary source of oxygen and a key component in the carbon cycle.
- Understanding the raw materials needed for photosynthesis helps in optimizing plant growth and developing sustainable agricultural practices.
What Are the Raw Materials Required by Plants for Photosynthesis?
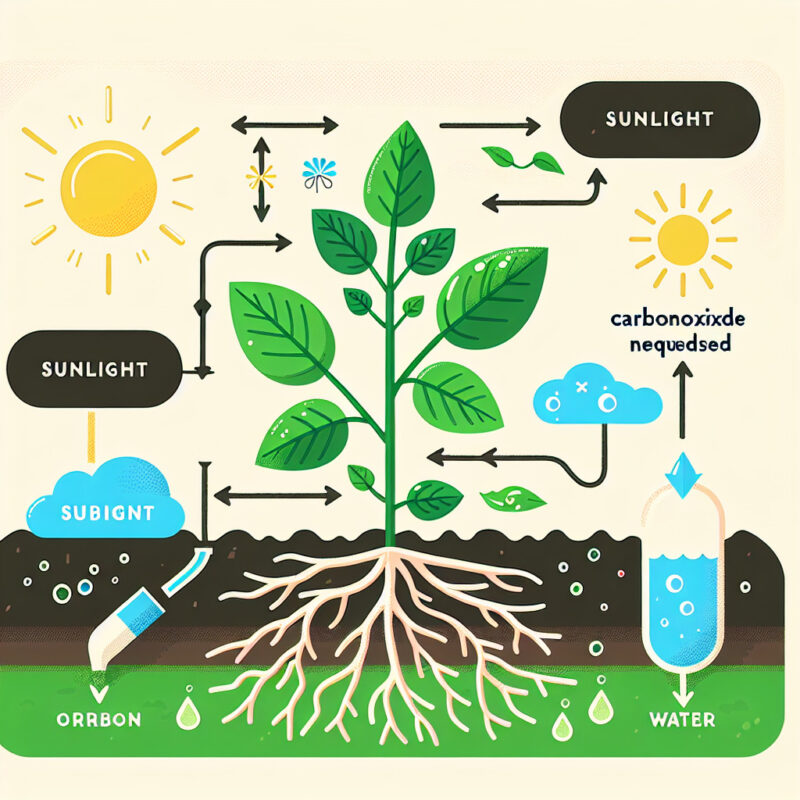
Photosynthesis is the process through which plants convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into glucose (a type of sugar) and oxygen. This vital process occurs in the chloroplasts, specialized cell structures found in plant cells. To carry out photosynthesis successfully, plants require specific raw materials.
Sunlight
Sunlight serves as the primary source of energy for photosynthesis to occur. Plants capture light energy using a pigment called chlorophyll, located in their chloroplasts. Chlorophyll absorbs light from the sun, particularly in the blue and red wavelengths, while reflecting green light, which is why plants appear green to our eyes. This absorbed light energy drives the chemical reactions necessary for photosynthesis.
Water
Water is another crucial raw material necessary for photosynthesis. It is taken up by plants through their roots and transported via specialized tissues called xylem. Water molecules split during photosynthesis through a process called photolysis, releasing electrons that help generate chemical energy. Additionally, water is crucial for maintaining the plant’s turgidity, essential for the function and structure of cells.
Carbon Dioxide
Plants obtain carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through tiny pores called stomata, mainly located on their leaves. During photosynthesis, carbon dioxide combines with water and light energy to produce glucose and oxygen. The carbon from CO2 is incorporated into glucose molecules, forming the basis for plant growth and development. Adequate levels of carbon dioxide are necessary to ensure efficient photosynthesis.
Mineral Nutrients
In addition to sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, plants require various mineral nutrients to carry out photosynthesis effectively. These nutrients are essential for the synthesis of important molecules within the plant, such as chlorophyll, enzymes, and proteins. Some critical mineral nutrients include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, calcium, and trace elements like iron, manganese, and zinc. These nutrients are often obtained from the soil through the plant’s roots.
Conclusion
Photosynthesis is a complex process that relies on specific raw materials for plants to convert light energy into chemical energy. Sunlight, water, carbon dioxide, and mineral nutrients are all vital components necessary for this essential biological process. Understanding the importance of these raw materials helps us appreciate the intricate relationship between plants and their environment, and highlights the critical role of photosynthesis in sustaining life on Earth.
FAQs
What are the key raw materials needed for photosynthesis?
In order to carry out photosynthesis, plants require three key raw materials: sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. These raw materials are essential for the synthesis of glucose, the primary product of photosynthesis.
Why is sunlight important for photosynthesis?
Sunlight plays a crucial role in photosynthesis as it provides energy for the process. Through a complex series of reactions, the chlorophyll pigments in plant cells absorb sunlight and convert it into chemical energy, which is then used in the synthesis of glucose.
How does water contribute to photosynthesis?
Water is essential for photosynthesis as it serves as a source of hydrogen ions (H+) and electrons (e^-). During the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis, water molecules are split, and their electrons and protons are used to generate energy-rich molecules like ATP and NADPH. These molecules are then utilized in the synthesis of glucose during the light-independent reactions.
What role does carbon dioxide play in photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a crucial raw material for photosynthesis. During the light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, plants utilize carbon dioxide to produce glucose. They extract carbon atoms from CO2 molecules and incorporate them into simple sugar molecules, which later combine to form glucose, the primary end product of photosynthesis.
What happens to the raw materials after photosynthesis?
After being utilized in photosynthesis, the raw materials undergo different processes. Sunlight continues to provide energy for other plant activities, while water may be further absorbed by the roots and transported to other parts of the plant for various functions. Carbon dioxide is released back into the atmosphere through respiration or used by other organisms for their own metabolic processes. The end product of photosynthesis, glucose, is either utilized immediately by the plant for energy or stored as starch for future use.
Exploring Different Photosynthetic Pathways
Types of Photosynthesis
Plants have evolved different strategies to carry out photosynthesis in various environmental conditions. Some plants, known as C3 plants, use the conventional C3 pathway where carbon dioxide is directly incorporated into the Calvin cycle. Others, like succulent plants and certain types of desert plants, have evolved alternative pathways. These include the CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) pathway and the C4 pathway.
The CAM Pathway
Plants utilizing the CAM pathway, such as cacti and succulents, are adapted to arid, water-limited environments. They open their stomata, through which carbon dioxide enters, during the night to minimize water loss through transpiration. The carbon dioxide is then stored as organic acids, which are later broken down during the day to release carbon dioxide for the Calvin cycle. This enables these plants to conserve water while carrying out photosynthesis.
The C4 Pathway
Plants using the C4 pathway have specialized leaf anatomy. They minimize water loss by reducing the time their stomata remain open. Carbon dioxide is initially incorporated into a four-carbon molecule, which is then transported to specialized cells where the Calvin cycle takes place. This allows C4 plants to efficiently capture carbon dioxide, conserve water, and perform photosynthesis even in hot and dry conditions.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, photosynthesis is a vital process for plants to produce glucose, their main source of energy. This process relies on three key raw materials: sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide. Sunlight provides energy, water provides hydrogen and electrons, and carbon dioxide provides carbon atoms for glucose synthesis. The raw materials undergo various transformations during photosynthesis, with the end product being glucose, which is used immediately or stored for future energy needs. Understanding the importance of these raw materials and the different photosynthetic pathways expands our knowledge of plant biology and how they adapt to different environmental conditions.