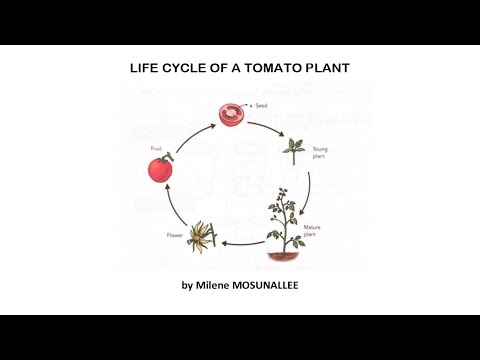
The life cycle of a tomato plant is a fascinating process that leads to the growth of a healthy, nutritious vegetable. Tomato plants have a unique life cycle that begins with sowing the seeds and ends with the production of fruit. In between, there are several stages of growth and development that must occur for the plant to thrive. In this article, we will explore each stage in detail, from germination to fruiting.Tomato plants are easy to grow and make for a great addition to any garden. Tomatoes are members of the nightshade family, related to both potatoes and eggplants. They can be grown in both traditional garden beds or containers. Tomatoes require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day, so they should be planted in a location that receives plenty of light. They also need well-draining soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8. To ensure good drainage, it’s important to mix organic matter such as compost into the soil prior to planting. Tomatoes should be planted deeply, burying at least two-thirds of the stem in the soil, as this encourages root growth and helps support the plant as it grows taller. Once planted, tomatoes need consistent watering throughout the growing season; however, they should not be over-watered or allowed to stand in wet soil. Fertilizer can also be beneficial for tomato plants; using a balanced 10-10-10 fertilizer will help provide necessary nutrients for healthy growth and fruit production. With proper care and attention, tomato plants can produce an abundant crop of delicious tomatoes throughout the growing season!
Germination of Tomato Seeds
Growing tomatoes from seed is an economical and rewarding way to add these popular vegetables to your garden. It is important to understand the process of germination for tomato seeds in order to have successful transplanting and growth. Tomato seeds require a specific amount of time and temperature in order to germinate successfully.
When it comes to growing tomato plants from seed, the two most important factors are soil temperature and moisture. The temperature of the soil should be between 18-30°C (65-85°F) for optimal germination. The soil must be kept consistently moist, but not waterlogged, until the seeds have sprouted. To encourage even moisture distribution, it is best to water gently from the bottom up using a shallow tray filled with water instead of directly onto the soil.
In addition, tomato seeds need darkness in order for them to germinate properly. If they are exposed to light during this process, their growth will be impaired and they will not grow into healthy plants. To ensure that your seeds receive adequate darkness while they are germinating, cover them with a thin layer of soil or use a seed starting tray with a clear lid that will keep out light while still allowing air flow.
Finally, tomato seeds require some amount of oxygen in order for them to grow properly. This can be achieved by lightly stirring the soil or compost in which they are planted before you water it. Additionally, when watering your tomato plants make sure that you do not overwater as this can cause oxygen levels in the soil to drop which can lead to root rot and other problems.
By following these steps you can ensure that your tomato seeds will germinate successfully and lead to strong, healthy plants for your garden!
Growing Tomato Plant
Tomato plants are very easy to grow and require minimal care. If you want to start growing your own tomatoes, the first step is to select a good quality tomato variety. Once you have selected your variety, the next step is to prepare the soil for planting. You will need to dig a hole that is twice as wide and deep as the root ball of the tomato plant. Add compost or manure to help nourish the soil and improve drainage. Once the soil is properly prepared, it’s time to plant your tomato seedlings or transplants. Place them in the hole and fill in around them with soil. Water thoroughly and add mulch around the plants to help retain moisture.
Tomato plants need plenty of sunlight in order for them to grow and produce fruit, so make sure they are planted in an area that gets at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight each day. They also need regular watering, especially during hot weather when they may need watering every day. Be sure not to over water or you may end up with damping off disease which can kill your plants. Feed your tomato plants regularly with a balanced fertilizer or compost tea for best results.
Once your tomatoes have started producing fruit, it’s important to keep up with harvesting them so that they don’t get too ripe and fall off the vine. If you’re growing indeterminate varieties, pruning may also be necessary for optimal growth and productivity. Prune away any stems or branches that are growing outside of where you want them, as well as any suckers that pop up between branches and stems. This will help promote air circulation which helps reduce disease problems and keeps growth under control so that all of your tomatoes have room to ripen properly without overcrowding each other on the vine.
Flowering Stage of Tomato Plant
The flowering stage of the tomato plant is one of the most important stages in the growth and development of the tomato crop. It is during this stage that the flowers are produced, which will eventually lead to the production of tomatoes. During this stage, there are a number of important activities that need to be carried out in order for the crop to reach its full potential.
One of these activities is pollination. Pollination is an essential process that must take place in order for fertilization to occur and for tomatoes to form. This process can be aided by various things such as wind, bees, and other insects. In order to ensure that pollination occurs properly, it is important to keep an eye on the environment around the plants and take measures to make sure that any pests or diseases do not hinder pollination from taking place.
The second activity that takes place during the flowering stage is pruning. Pruning is necessary in order to remove any dead or diseased leaves or branches from the plant. This helps ensure that there is enough space for new growth and keeps the plants healthy and strong. It also helps remove any excess foliage which might prevent light from reaching parts of the plant where it needs to in order for photosynthesis to occur properly.
Finally, once all these activities have taken place, it’s time for harvesting! When all conditions are right, you should expect tomatoes to start forming within about two weeks after flowering has begun. At this point you can begin picking them as soon as they reach their desired size or coloration but make sure not to pick them too early! Doing so will result in an inferior product with less flavor and texture than if you had waited a bit longer before harvesting.
Fruit Development of Tomato Plant
Tomato plants are a member of the nightshade family and produce a fruit-like vegetable. The process of fruit development in a tomato plant is quite complex and involves both the flower and the stem. During flowering, the ovary of the tomato plant produces small flowers that contain pollen grains. When these pollen grains are exposed to air, they are able to fertilize the ovary, triggering its development into a tomato fruit. Once the ovary has been fertilized, it begins to swell and grow in size as it produces enzymes that help break down starch into sugar and convert it into energy for growth. As the ovary continues to grow, it forms septa which divide it into segments called locules. In each locule, an ovule is formed which will eventually become a seed if fertilization occurs.
As the tomato plant flower develops, its petals will eventually drop off and expose the stigma which is covered with sticky nectarines that attract pollinating insects, such as bees or butterflies. These insects pick up pollen from other flowers as they fly around and deposit them onto the stigma of the tomato flower. This pollen then travels down through a long tube called a style to reach an ovule in one of the locules on the developing tomato fruit. If this process is successful, then fertilization occurs and seeds begin to form inside each locule of the tomato fruit.
In addition to seed formation, other processes occur as well during fruit development such as cell expansion which causes enlargement of cells within both fleshy parts as well as in seeds themselves. This cell expansion leads to an increase in size of both seeds and fleshy parts like skin and pulp which gives tomatoes their characteristic shape and texture when ripe. Finally, ripening also occurs during this stage where tomatoes turn red due to increased levels of lycopene being produced by cells within their skin; this also helps contribute to their sweet flavor when eaten ripe from vines!
Overall, fruit development in tomatoes is a complex process that involves both floral structures and changes within individual cells that lead to formation of seeds as well as changes in color and flavor when ripe!

Setting and Ripening of Tomatoes
Tomatoes are one of the most popular vegetables in the world. They are a versatile ingredient used in a variety of dishes, from salads to sauces. Knowing how to set and ripen tomatoes correctly is essential for getting the best flavor and texture from your tomatoes. To help you get the most out of your tomatoes, here are some tips on setting and ripening tomatoes.
When setting tomatoes, you want to make sure they are well-drained and exposed to plenty of direct sunlight. Tomatoes like warm temperatures, so avoid placing them in cold or shady areas. When planting tomatoes, use a soil mix that is rich in organic matter and allows for good drainage. If possible, plant your tomatoes in raised beds or containers so they can be easily moved if needed.
When it comes to ripening tomatoes, you want to give them enough time on the vine for maximum flavor and sweetness. Depending on the variety of tomato, this can take anywhere from 2-4 weeks after they have set fruit. As they ripen, their color will change from green to deep red or yellow depending on the variety. If you want your tomatoes to last longer once harvested, store them at room temperature away from direct sunlight until ready to use.
Following these tips will ensure that you get the best results when setting and ripening your tomatoes. With proper care and attention, your tomatoes will be full of flavor and sweetness that will add deliciousness to all kinds of dishes!
Harvesting Tomatoes
Harvesting tomatoes can be a fun and rewarding experience. It is best to harvest them when they are ripe and full of flavor. If left on the vine too long, they can become mealy and tasteless. To harvest tomatoes, you will need to select only those that are deep red in color, firm to the touch, and have no soft spots or blemishes. You should also avoid harvesting any tomatoes that are still green or yellow in color, as these are not yet ripe and will not taste as good.
Once you have selected your ripe tomatoes, it is important to handle them with care. Gently pull the tomato off of the vine without twisting or turning it. If you twist or turn it too much, it can break off prematurely and leave behind a stem that will continue to produce more fruit. You should also avoid stacking multiple tomatoes on top of each other as this can cause bruising and damage the tomato’s skin.
Once you have harvested your tomatoes, you should store them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. This will help keep them fresh for longer periods of time. It is also important to remove any stems before storing the tomatoes as they can harbor bacteria which can cause spoilage over time. When storing your tomatoes in a refrigerator, make sure to keep them in an airtight container so that moisture does not collect around them which could cause mold or spoilage.
Harvesting tomatoes at the peak of ripeness is essential for getting the best flavor out of your crops. By following these simple tips, you can ensure that your harvest lasts longer and tastes better than ever before!
Common Diseases and Pest Control for Tomato Plants
Tomato plants are susceptible to a variety of diseases and pests. Common diseases of tomato plants include fungal infections, bacterial spot and blight, anthracnose, early and late blight, and verticillium wilt. Fungal infections can be prevented by keeping the leaves dry and avoiding overhead irrigation. Bacterial spot and blight can be controlled with fungicides or copper-based treatments. Anthracnose can be prevented by selecting resistant varieties or using fungicides. Early and late blight can be prevented through crop rotation and sanitation practices such as removal of infected plant material. Verticillium wilt is a soil-borne fungus that cannot be controlled with fungicides; instead, it is best managed through crop rotation and selecting resistant varieties.
In addition to common diseases, tomato plants are also subject to various insect pests including aphids, flea beetles, cutworms, whiteflies, Colorado potato beetles, hornworms, stinkbugs, thrips, leafminers, tomato fruitworms, mites, slugs and snails. Effective pest control measures include using row covers or floating row covers to keep pests away from the plants; using companion planting to attract beneficial insects; applying insecticidal soaps or horticultural oils; using traps such as sticky cards or yellow sticky boards; monitoring populations regularly; and hand-picking any visible pests.

Conclusion
The tomato plant has a fascinating life cycle! It starts with a seed, which is planted in the soil and germinates to grow into a young plant. As it grows, it needs sunlight, water, and nutrition from the soil to survive and produce flowers. After pollination, the flowers form fruits that are green until they ripen and turn red. As the fruits mature, they can be harvested for culinary use or replanted to start another life cycle. The tomato plant is an important crop around the world and provides us with tasty fruits!
In conclusion, the tomato plant has a complex life cycle that starts from seeds and finishes with fruits. It needs sunlight, water, and nutrition from the soil in order to grow properly. The tomatoes produced by this plant are an important source of food in many parts of the world and offer a delicious addition to any dish!